The Threat of a Boron Market Shortage
The global boron market is experiencing a shortage that will impact several industries. The demand for this strategic material is projected to increase significantly due to its use in multiple industries and applications, from advanced energy to decarbonization and food security.
What is Boron
Boron is a metalloid element found in minerals and rocks, usually combined with other elements such as oxygen or magnesium. Boron is also present in seawater, but only at deficient levels. Plants absorb boron from the soil and use it to build strong cell walls. Animals that eat plants can also get boron in their diet.Applications and Demand for Boron
Boron is a crucial element in many industrial and military applications. It is used as a dopant in semiconductors, an agent in pyrotechnics, and a neutron absorber in nuclear reactors. For health, Boron is also an essential component of growth and the maintenance of bones. Boron helps heal wounds and increases the body’s use of estrogen, testosterone, and vitamin D. It boosts magnesium absorption, lowers inflammation, and raises antioxidants. Boron protects against pesticides and heavy metals and improves brain electrical activity, cognitive performance, and short-term memory. For many years and even today, boron’s primary commercial uses have been for glass and ceramics manufacturing with improved strength and durability. Boron reduces glass viscosity to create smooth surfaces and lower thermal expansion for professional catering and laboratory use. These glasses and ceramics are also widely used in phones, cars, and house construction. Boron can also be used as an additive to solar panels, where it plays a critical role. It decreases the reflexivity while increasing the efficiency of panels. The solar market is expected to grow at more than 20% per year until 2026. Furthermore, by 2050, wind and solar are expected to generate up to 70% of the world’s electricity. With electricity generation increasing 2.5x over the same period, boron’s use in both technologies will undoubtedly be a huge boon to the industry. Also, boron is an essential component in the production of neodymium magnets. Currently, Boron is only produced in a few countries. Like lithium, boron has a small supply chain with limited resources, but demand is rapidly increasing, for instance, for use in powertrains in electric vehicles. 5E Advanced Materials (FEAM) estimates that various boron compounds make up around 2.5% to 3% or 46 kg to 50 kg of an EV weight. It is expected that the EV market will grow from approximately 6.3 million units sold in 2021 to between 26.8 million and 34.8 million by 2030. Its use in EVs appears to be another area of explosive growth. However, EVs aren’t the only use for permanent magnets; all modern vehicles use them to some extent. They are used to improve fuel efficiency by assisting with crankshaft rotation. Other applications include the manufacture of various electronics, disc drives, and actuators. Samarium-cobalt magnets are the most common alternative to neodymium magnets, but they are typically used only in the defense and aerospace industries. The market for permanent magnets is currently projected to grow to $23.4 billion by 2027, from $16.4 billion in 2021.Boron in Future-Facing Applications
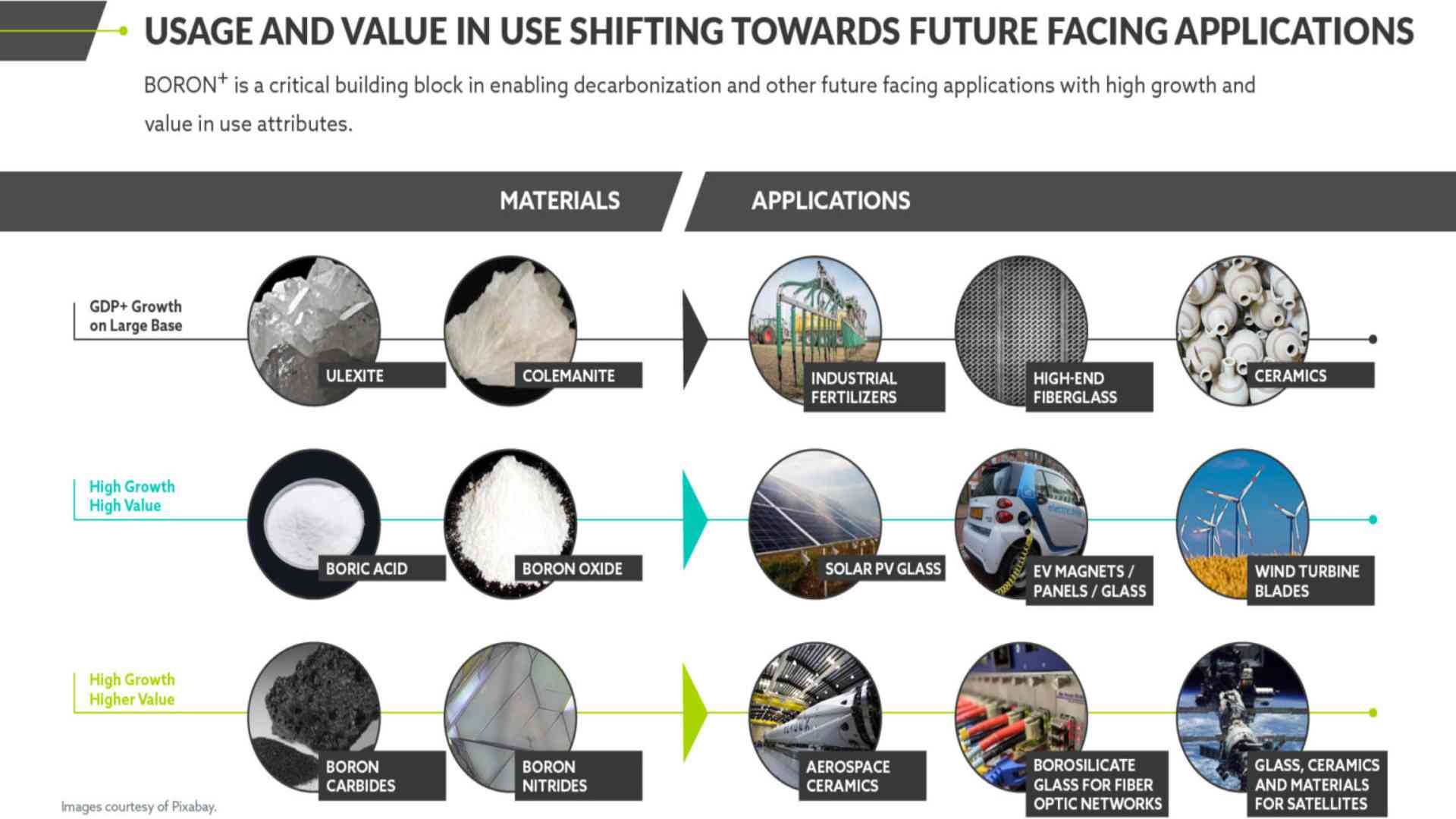 Source: https://5eadvancedmaterials.com/wp-content/uploads/5EAdvancedMaterialsBoron101Infographic2_14Jan22-1536×764.jpg
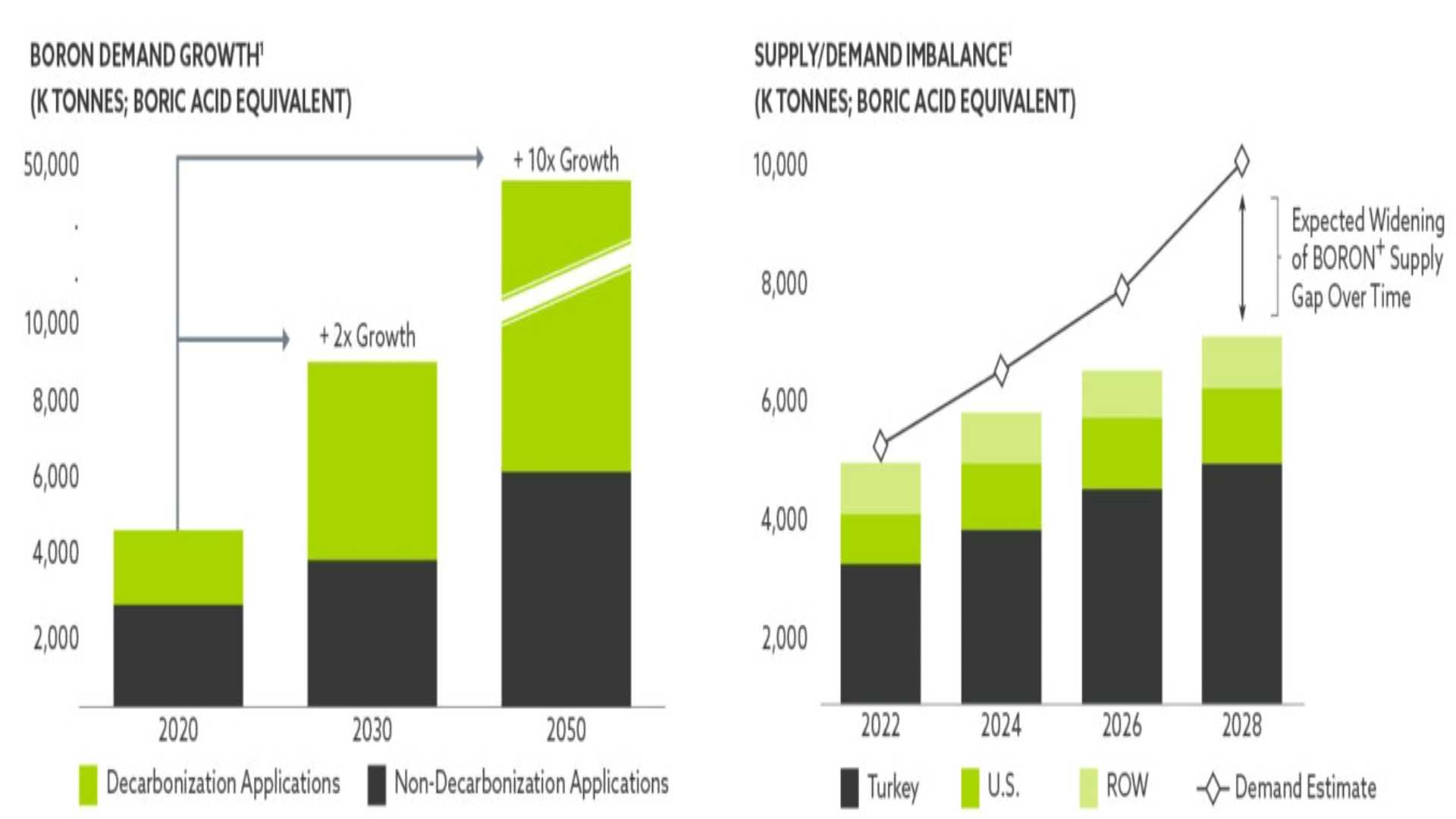
It seems like the boron market will grow steadily over time. For now, the production gradually declines as existing deposits deplete, which results in an imbalance between demand and supply, leading to higher prices like $1,250 per tonne, exceeding previous estimates of $739 per tonne.
Credit Suisse predicts that boron demand will rise significantly within three years. As a result, the relative need for boron will increase rapidly, and these elevated prices are likely to continue.
Source: https://5eadvancedmaterials.com/wp-content/uploads/5EAdvancedMaterialsBoron101Infographic2_14Jan22-1536×764.jpg
It seems like the boron market will grow steadily over time. For now, the production gradually declines as existing deposits deplete, which results in an imbalance between demand and supply, leading to higher prices like $1,250 per tonne, exceeding previous estimates of $739 per tonne.
Credit Suisse predicts that boron demand will rise significantly within three years. As a result, the relative need for boron will increase rapidly, and these elevated prices are likely to continue.
 Source: https://5eadvancedmaterials.com/boron-101/
With glass and ceramics manufacturing accounting for approximately half of boron’s commercial usage and fertilizer accounting for about 20%, there is plenty of growth in boron’s emerging uses. Solar panels, neodymium magnets, and advancements in advanced materials all offer explosive growth opportunities that significantly reduce the element’s reliance on existing revenue streams. However, there may be even more opportunities for boron’s use to expand as new applications for the element emerge.
According to Credit Suisse, boron demand could grow more than tenfold by 2050 under a high-growth scenario. At that point, decarbonization technologies would account for more than 90% of boron demand. A sector that currently accounts for only a small portion of boron’s current demand is positioned to become the most important.
While the next five years appear promising, the next couple of decades could be a game-changer for the boron market. So, perhaps it’s not just the short-term that investors should concern themselves over. With this in mind, now could be a great time to get involved in this exciting industry.
Source: https://5eadvancedmaterials.com/boron-101/
With glass and ceramics manufacturing accounting for approximately half of boron’s commercial usage and fertilizer accounting for about 20%, there is plenty of growth in boron’s emerging uses. Solar panels, neodymium magnets, and advancements in advanced materials all offer explosive growth opportunities that significantly reduce the element’s reliance on existing revenue streams. However, there may be even more opportunities for boron’s use to expand as new applications for the element emerge.
According to Credit Suisse, boron demand could grow more than tenfold by 2050 under a high-growth scenario. At that point, decarbonization technologies would account for more than 90% of boron demand. A sector that currently accounts for only a small portion of boron’s current demand is positioned to become the most important.
While the next five years appear promising, the next couple of decades could be a game-changer for the boron market. So, perhaps it’s not just the short-term that investors should concern themselves over. With this in mind, now could be a great time to get involved in this exciting industry.
Boron Supply Profile
Presently, the boron supply chain is relatively weak. Turkey accounts for 60% of global boron sales, with state-owned Eti Maden controlling the production. Eti Maden and Rio Tinto (RIO), which produces most of its boron in the United States, contain 85% of the total boron supply. “You can literally count all the boron deposits in the world on the one hand,” says Tim Daniels, CEO of Erin Ventures. The graph below depicts all of the boron projects that aim to go into production shortly.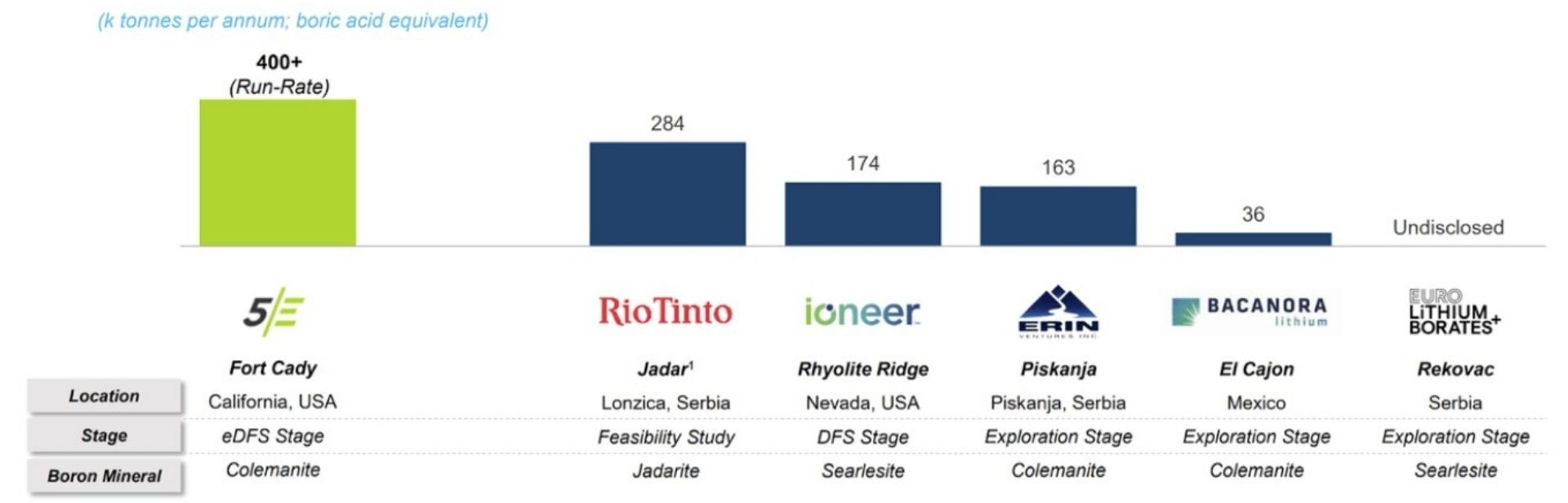 Source: https://5eadvancedmaterials.com/boron-101/
5E Advanced Materials’ Fort Cady asset represents a required source of incremental borates supply in the United States (and likely globally) that is distinguished by its highly convenient location for domestic consumption (as opposed to obtaining from overseas, specifically Turkey, which supplies 84% of boron-related imports per the USGS). It has the smallest environmental footprint, with additional ESG initiatives in the works (solution extraction, geothermal potential).
Source: https://5eadvancedmaterials.com/boron-101/
5E Advanced Materials’ Fort Cady asset represents a required source of incremental borates supply in the United States (and likely globally) that is distinguished by its highly convenient location for domestic consumption (as opposed to obtaining from overseas, specifically Turkey, which supplies 84% of boron-related imports per the USGS). It has the smallest environmental footprint, with additional ESG initiatives in the works (solution extraction, geothermal potential).





