Boron Podcast – Introduction to Boron Mining
Introduction to Boron Mining
Boron was named after the mineral borax, thought to come from the Persian name burah for the mineral. There are over 200 minerals that contain boron, but only a few minerals such as colemanite and borax are commercially important.
How Long Has Boron Been Traded?
Borax was first extracted from dry lake beds in Persia and Tibet and traded to Arabia and India over a thousand years ago.
History of Boron Ore Mining
The mining of boron ore has a long and fascinating history. The earliest known production dates back to 1878 when the United States Geological Survey found high-grade deposits in California’s Death Valley region.
It was not until 1906 that commercial mining began; however, it did not last for more than three years due to heavy competition from nearby mines at Trona Pinnacles and Searles Lake as well as financial difficulties during World War I which caused its closure shortly after 1916.
In 1926 another attempt had been made by Vanadium Corporation with little success because regulations required an expensive treatment process before export could take place.
How Boron’s Benefits Became Appreciated
In the early days, it was discovered also that in large quantities, Borax would cause a person to go into shock. It also caused severe irritation and dry skin among those who used this product on their clothes or other items to whiten them. This led many people at first to mistrust boron given the potential harmful effects on boron compounds could be for one’s health.
Everything changed, however, as scientists took notice of its properties such as detergent building agents which are very useful nowadays due to more environmentally friendly products becoming available over time whose effect is less harmful than common bleach chemical treatments.
Where Boron is Mined
Borate deposits are associated with volcanic activity and arid climates, with the largest borate deposits located in three locales: the Mojave Desert of the United States, the Tethyan belt in southern Asia, and the Andean belt of South America. As a result, most borates are extracted primarily in Turkey and California, and, to a lesser extent, in Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, China, and Peru.
The largest global borax deposits known, many still untapped, are in Turkey. Global proven boron mineral mining reserves exceed one billion metric tonnes. Yearly production is about four million tons.
In Turkey, the minerals colemanite and rasorite (kernite) provide for most of this being mined primarily from the provinces Eskişehir Kütahya and Balıkesir.
The United States holds nearly one-fifth of the world resources of boron, is a net exporter. U.S. Borax operates California’s largest open-pit mine in Boron, California, one of the richest borate deposits on the planet. There are also promising operations scaling up in Fort Cady, California operated by American Pacific Borates, recently listed on Nasdaq and renamed to 5e Advanced Materials.
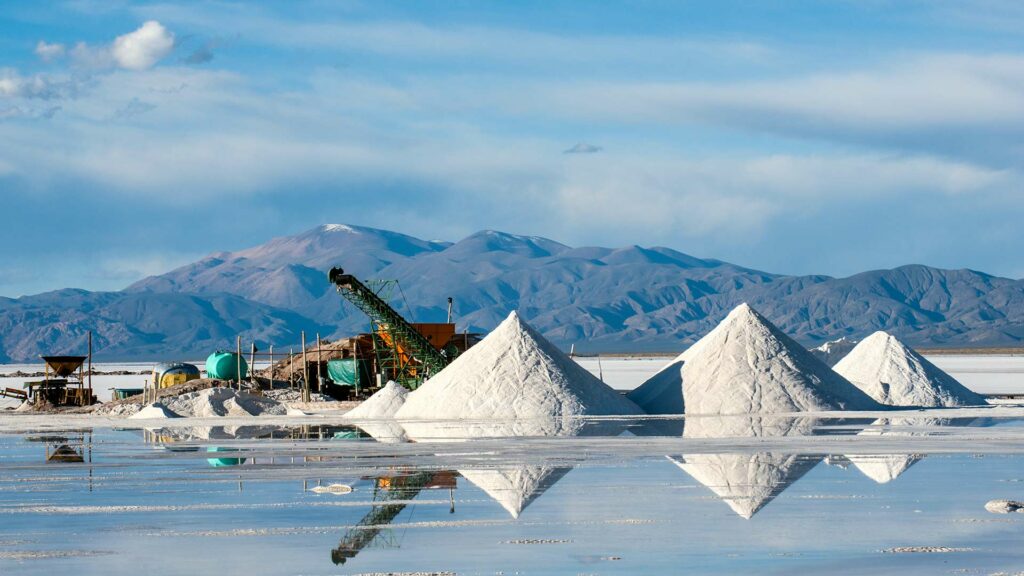
How Boron is Mined
Several steps are needed to extract Boron for commercial purposes.
Dissolving
Crushed ore is mixed with hot liquor in a combination of borates and water. The borates dissolve in the water. Insoluble rocks, sand, and other solids are then removed using screens.
Settling
The saturated borate solution is pumped into large settling tanks, called thickeners. Heavier clay settles to the bottom of the tank, leaving the liquor on top.
Crystallizing
The liquor is transported to tanks, called crystallizers, to be cooled. The drop in temperature forces the borates to crystallize, forming a slurry of borate crystals and water.
Filtering
The slurry is poured over special fabric filters and washed to ensure purity. Water is drawn away by a vacuum beneath the filter.
Drying
Damp borate crystals are then transferred to huge rotating dryers that use hot air to finish the crystal drying process.
Conveying
Dry borates drop onto a conveyor belt to be transported for storage or packaging and shipping.
Boron is present in the environment via natural and human-made processes. Natural weathering of soils and rocks can release it into the air, water, or soil. Manufacturing plants that use boron (like glass manufacturing and coal-burning power plants) also release it.
Once it is in the environment, it does not break down. Rather, the element changes form or attaches to or separate from the soil, sediment, and water particles.
Boron is an essential nutrient for aquatic life and terrestrial plants, but at high concentrations, it can have toxic effects. Concentrations of boron observed in Minnesota’s surface waters are typically lower than the level that would harm aquatic life.
The Growing Influence of Boron
Boron is used in multiple applications and industry sectors with global scale of production and distribution. There are important implications for our planet’s ecosystems and climate change. To tap into this resource-rich market, many countries have expanded domestic production
This causes significant environmental damage, including acid mine drainage from sulphidic ores used by some regions’ coal plants, air pollution, water contamination. The latter releases heavy metals during ore processing along waterways while also contributing substantially to greenhouse gas emissions due to reliance on fossil fuels for energy purposes.
There is also an ongoing debate about the effects of boron mining on our environment. The impacts are complex and vary depending on contextual factors such as geography, geology, climate change scenarios, socio-economic status of communities in proximity to mines sites.
One serious impact of mining on the environment comes from high water consumption and consequent depletion of water resources as well as air pollution (fumes) involved in extraction.
Critics claim practices lead to environmental degradation by way of contamination or resource depletion. However, others point out that there may be economic benefits for some stakeholders involved like governments and local people who work at these mine sites so they can improve lives through increased income opportunities from employment in this industry.
Boron Today
Today, Boron is used as an ingredient in multiple applications and products including (borosilicate) glass, ceramics, and enamels, as well as fiberglass for insulation. Recently, boron has become a strategic mineral known for its superconductive properties and is used in EV batteries, neodymium magnets in wind turbines and for tensile strength in the automotive and construction industries. Other sues include protective coatings and anti-corrosion, and in the nuclear power industry, boron plays a safety tole given its ability to deflect radiation.