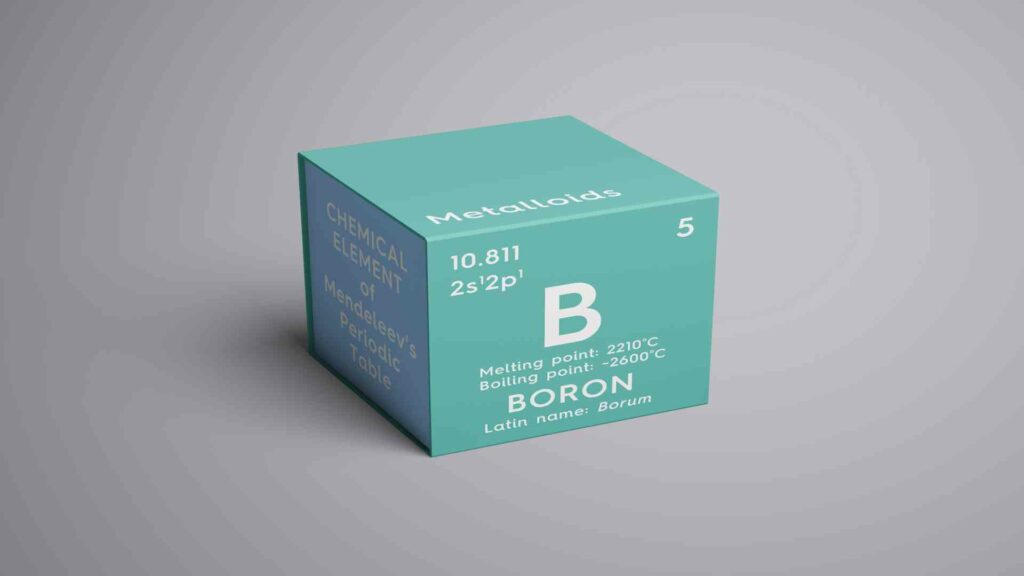
Boron absorbs infrared rays
It has three different absorption peaks for infrared rays. The first and second are at wavelengths of about 12 microns, while the third is around 19 microns. This means that it absorbs both long-wave radiation and short-wave radiation emitted from our nearest star. But it does not absorb visible light very well in comparison to these other types of radiation. Importantly, this makes it a great material for solar panels as they can be built more efficiently with lower production costs.
Boron’s applications in energy efficiency
It absorbs infrared radiation, which leads to applications related to energy efficiency.
Energy-efficient homes
Energy-efficient homes and buildings use boron insulation for their walls or roofs. This helps reduce the need for air conditioning systems in hot climates by reducing heat transfer into the building from outside.
It does a great job absorbing infrared rays. Hence, they are often useful on roofs or walls. The property that makes Boron such a good absorber for these kinds of rays also makes them effective at keeping heat out. If you have an attic space with thick insulation and enough ventilation, adding some material can help. It prevents your home from getting too hot in the summer. In climates where winter brings cold air indoors installing boron sheets will help. It can stop all those cold drafts coming through cracks around windows and doors. You can save both money and fuel costs by a great amount.
It is discovered that boron absorbs infrared rays. You can use it to make windows more energy-efficient. It acts as a heat-reflecting barrier on the outside while still allowing light through on the inside. Therefore, it is very helpful for window manufacturers.
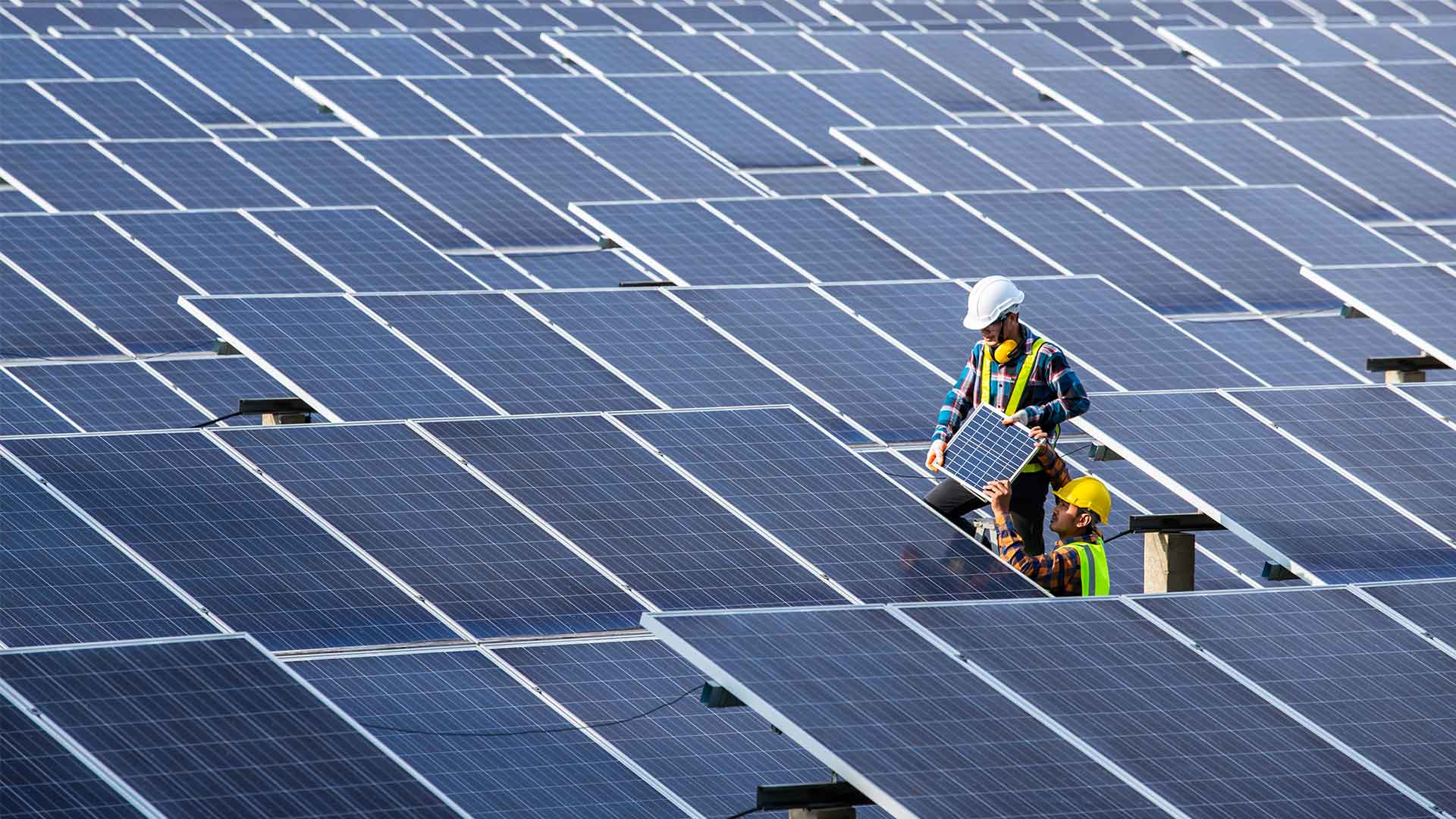
Solar Panels
The crystalline structure of Boron produces solar panels. It increases output six percent per 100 degrees Celsius (at room temperature). If this could be applied elsewhere, there are many potential benefits.
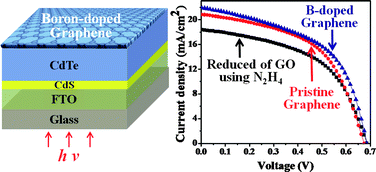
A lot of the energy we use goes towards heating and cooling. Hence, it is important to keep this in mind when building solar panels.
The use of boron in the production of solar panels also lead to new ways to generate electricity from sunlight.
It is generally present in a form of crystal called boron nitride. This type of crystalline structure is useful to absorb infrared radiation and can help improve energy efficiency, among other applications.
Semiconductor industry
The absorption of infrared rays is a critical factor in industries such as the semiconductor industry. It is useful in these industries and is an effective absorber of infrared radiation.
The infrared absorption properties of boron are an avenue that is useful to new technologies. Like superconductors, thermoelectric converters, or lithium-ion batteries with high energy density.
It is useful in helping protect semiconductors from heat damage. When boron is applied, it helps eliminate the effects of infrared radiation and prevents components from being overheated. It also protects solder from melting or blowing off in an area where a temperature reaches 120 degrees Celsius (248 Fahrenheit).
Fiberglass insulation
Another big use for boron and compounds is fiberglass insulation. Because they absorb a lot more heat than their counterparts like cotton or wool. So this property helps make homes more energy efficient even if drafts are coming through cracks around windows or doors. They are also porous to let air circulate better. So less hot air gets stuck inside your home.
They do not have adverse effects on heating and cooling systems like other types of insulation do. This is because it only absorbs infrared radiation. Additionally, it does not interfere with the transfer of heat energy like other materials that contain asbestos, for example.
Lasers
It’s ability to absorb infrared rays also means that some types of lasers use this element as a medium to produce laser beams. The lasers that emit infrared wavelengths help in cutting metal, welding plastics, and as a medical tool.

The use of Boron is not limited to just solar panels. It is also useful for laser cutting and welding because it absorbs infrared rays from the lasers. This means that these types of operations do not need any other type of protective material on top, which does make things easier. Infrared radiation is a form of energy in the electromagnetic spectrum between radio waves and visible light. So this absorption allows Boron to store heat better. It is comparatively better than exposure to sunlight as well as reduces cooling costs by up to 50%.
Cooking Time
Boron also has applications in cooking as it reduces hot spots on pans. This saves time and provides more even heating when you need to cook up a meal quickly. Or when you cook over an extended period (maybe shorter than normal due to reduced hotspots).
It absorbs infrared rays and reduces cooking time by 70%. We can see how effective boron when you apply it in cooking processes like preserving vegetables. Especially, when you are cooking through using an oven with the door slightly open. You will see that your food will cook faster and in a healthier way.
Boron ensures that veggies are cooked faster and more efficiently. You may also notice that these preserved fruits and/or vegetables will retain their natural color better. Because less UV light can penetrate them. It doesn’t only apply when cooking though; there are plenty of engineering applications as well. One such application would be refrigeration cooling systems, where we see an increase in efficiency from up to 50%. If you use boron in your refrigeration cooling system, you do not need to use as much electricity or gas.
Boron is a great insulator of heat. And it has many applications that can make the world more energy-efficient. We all need to consider this element when we are trying to save our planet by going green. So don’t forget about Boron next time you’re using solar power or any type of alternative energy source.
Other energy-efficient applications
Boron has a cost-effectiveness factor that makes it an attractive option even if not as environmentally friendly as other options like natural gas or electricity produced with renewable sources like wind or solar.
Boron is also useful in low emission diesel engines. Here it reduces nitrogen oxide emissions by up to 80%. This has the potential of reducing health risks and improving air quality for nearby populations.
And finally, boron’s abilities as a neutron absorber make it attractive for nuclear power plants. It is due to its ability to reduce radioactive waste particles (and other hazardous materials) from escaping into the atmosphere.
Boron has many practical uses besides insulation or cooking utensils. Because it absorbs infrared rays. So there are many more possibilities than just these few examples.
There are many other uses of Boron that we have yet to discover. But what is certain at this point is that it is an economically viable option with plenty of applications.
Conclusion
In summary, the use of boron in windows and other building materials is promising. It can help reduce global energy consumption. The material has a wide range of potential applications, from construction to spacecraft and more. It is especially good for buildings because it helps maintain indoor air quality while also providing natural light.