Boron and Healthcare
Boron is an essential mineral that is found in our food supply naturally, and many of us consume boron for health without knowing we are doing so. Boron is present in eye drops and supplements for bone development, osteoarthritis treatment, muscle building, testosterone level increase, aid cognitive function, and strength improvement. It’s also beneficial for women’s health to relieve menstrual cramps and reduce vaginal yeast infections.
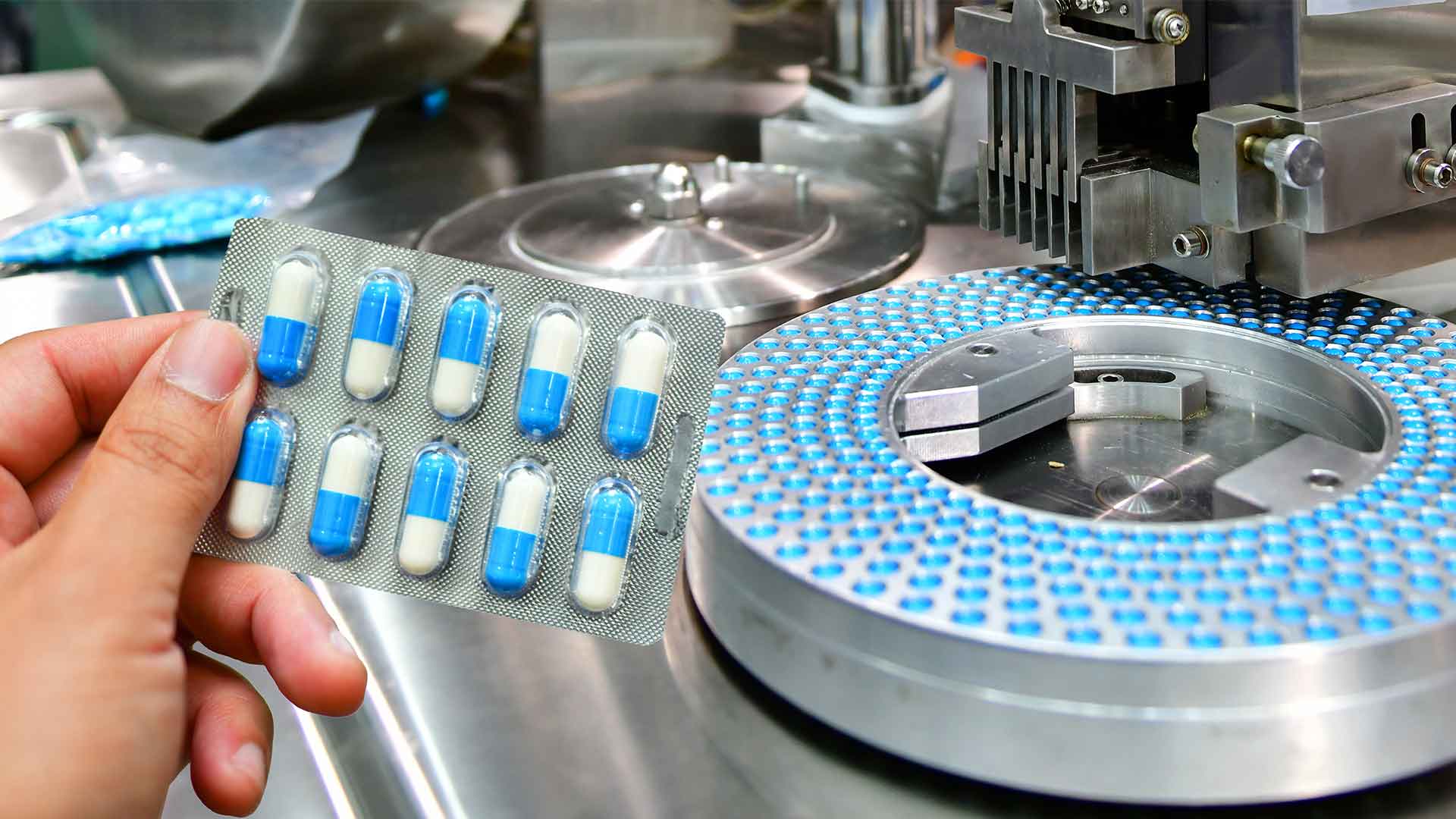

The most common form of boron in pharmaceutical products is boric acid. Boric acid can be crushed into a powder from its natural form. Boron compound derivatives, known as hydrogen Borate (H3BO3), are weak acids that are derived from the mineral Boron. They are widely used in over-the-counter antiseptics or astringents.
Let’s Take a Look at Boron in Eye Care
Boron is commonly used in eye care products. Boric acid eyewashes have been on the market for many years to treat irritation and prevent infection. Eye-care products contain a safe and balanced amount of borates, so there are no risks from consuming more than the recommended daily intake.
Eyewashes are made in an isotonic salinity solution, which consists of purified water and sodium chloride (salt). The safest form of boron eye drops contains 0.12mg per drop, although the recommended daily dose is likely to be higher.
Boron has multiple benefits in eyewash: It may inhibit bacterial or fungal growth and help prevent some mild infections.
It is compatible with your eye tonicity: This means that drops do not dilute or diffuse essential chemicals within your eye fluid because it doesn’t disrupt the natural eye chemistry.
It functions as a buffering ingredient: Buffering agents are able to maintain the pH balance in a solution, even when alkaline or acid are added. You can add inactive or active ingredients to your solution, but they won’t alter the pH balance.
Boron Helps Women’s Health
Boron appears to alter how the body processes other minerals such as calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus. It may increase estrogen levels in both older women, especially post-menopausal women, and healthy men. Estrogen has been shown to support healthy bones and mental function. Boric acid (a common form of Boron) can kill yeasts that cause vaginal problems.
The painful symptoms of menstrual cramps or dysmenorrhea can be alleviated using boron. Research has shown that taking 10 mg per day by mouth during menstrual bleeding can reduce pain in young women who experience painful periods.
As for vaginal yeast infections, when used inside the vaginal area, boric acid has been shown to treat yeast infections candidiasis successfully. But opinions differ as to the efficacy and safety of the treatment.
Boron is Also Used to Help Treat Cancer
Boron is used in anticancer drugs to treat multiple myeloma relapses and mantle-cell lymphoma. Boron is directly responsible for binding the catalytic location of the 26S proteasome, a protein complex that is susceptible to the development of cancer.
Boron Neutron Capture Therapy or BNCT has been used in cancer treatment for a number of years where radiation and chemotherapy have limitations. It relies on the use of neutrons for the generation of energetic alpha particles to destroy cells within the tumor, but not in the surrounding tissue.
BNCT uses boronated agents to deliver boron-10 to tumors, which, after undergoing irradiation with neutrons, yields litihium-7 and an alpha particle. The alpha particle has a short range, affecting tumor tissues rather than the more distal normal tissues.
To fully realize the clinical potential of BNCT, however, improvements in existing localized delivery agent systems or new compounds that target tumors are still necessary.
Boron-10 is also being used in experimental research related to the field of radiotherapy. It may be helpful in certain medical conditions to destroy or weaken abnormal cells. This relatively new procedure, still experimental, uses Boron-10. Boron-10 is concentrated on the malignant tumor and the patient is then exposed to neutrons, which are strongly absorbed in boron, producing high-energy beta particles that can kill cancer.
Let’s Talk a Little About Myeloma
Advances in research into Myeloma or bone marrow cancer promote greater use of boron in Medicinal Chemistry. For medicinal chemists, Bortezomib (Velcade®), a dipeptide boronic acid approved by the FDA in 2003, treats multiple Myeloma
Research into proteasome inhibitors which resulted in Myeloma treatment, has opened the doors to discovering further Boron-containing compounds. Boron compounds have been approved for use in the treatment of nail fungus for instance (onychomycosis) under the Tavaborole brand for example and Eucrisaborole for mild to moderately severe atopic dermatitis.
Boron for Therapeutics
Despite boron’s proven ability to destroy biological targets and offer medical chemists an opportunity to develop new areas for drug discovery, the medicinal chemistry community has been reluctant to use boron because of the risks and lack of synthesizing boron-containing substances.
Diazaborines is one class of boron-containing compounds that are being evaluated in the field of therapeutics. Dewar, an investigator of the ‘nonbenzenoid’ aromaticity heterocycles, synthesized diazaborines for the first time. Dewar’s work provides the first evidence of antimicrobial activities for a compound containing boron.
Diazaborines possessing antibacterial activities have been awarded numerous patents with Sandoz Pharmaceuticals publishing numerous evaluation studies and is a promising research area for further use of boron compounds in microbiology.