Baking Soda and Borax
Baking Soda and Borax are two of the most popular household products. They both are naturally occurring salts with many other similarities. So, which one is better? And what’s the difference?

Baking soda
About Baking Soda
Baking soda is a common household ingredient that can be used for various purposes, including cleaning, cooking, preserving, and baking. It’s also known as sodium bicarbonate or simply bicarb.
While most people are familiar with its uses around the home, this has many health benefits. For example, it can be used as a natural antacid to relieve indigestion or heartburn. Additionally, this is effective in treating acne and other skin conditions.
Baking soda is also used to absorb moisture, neutralize odors and scour surfaces. It can make cakes and muffins rise and keep the refrigerators smelling fresh.
When used correctly, this compound is a safe and effective way to clean, cook, and bake. However, it’s important to exercise caution when using this substance, as it can irritate if not used properly.
Natural Sources of Baking Soda
The natural mineral of sodium bicarbonate is nahcolite, whose deposits can be found in Colorado’s Eocene-age (55.8–33.9 Mya) Green River Formation, Piceance Basin. During times of high evaporation within the basin, nahcolite was accumulated as beds. It is industrially mined similarly to coal mining, using common underground mining strategies like bore, drum, and longwall mining. It is also mined by pumping boiled water through nahcolite beds and crystallizing the dissolved nahcolite using a cooling crystallization process.
Other Uses
- As a pest control measure
- To increase the alkalinity of water sources
- As a mild disinfectant
- As a neutralizer for acids and bases
- As the main component of black snake fireworks
- As a fire extinguisher
- As an inhibitor of fungi growth in agriculture
- As a cattle feed supplement
- As an antiseptic for preventing infections
- As an ingredient in mouthwashes and deodorants
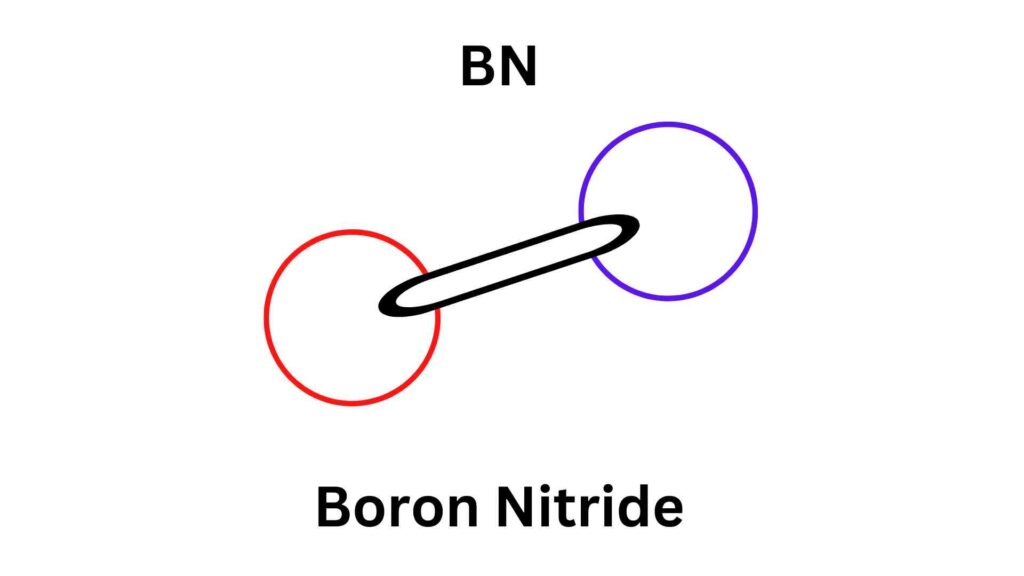
About Borax
Borax, also known as sodium tetraborate, is a common name for anhydrous or hydrated sodium borate. It is commonly used for decahydrate sodium borate, and so its chemical formula is Na2B4O7·10H2O with a molar mass of 381.38 g/mol.
Borax, unlike baking soda, is mined rather than manufactured, and the vast majority of this compound is obtained from dried-up lakes in California and Turkey.
Borax is an effective cleaning product for the same reasons that baking soda is effective; it is alkaline and abrasive. It can be used to clean drains, clean dishwashers, deodorize carpets, and eliminate rust stains. It’s also useful for killing weeds and letting go of pesky bugs (such as cockroaches). And, unrelated to cleaning, it’s a key ingredient in making slime, a hugely popular activity among kids.
Furthermore, this compound is easily converted into boric acid.
Na2B4O7·10H2O + 2 HCl → 4 H3BO3 + 2 NaCl + 5 H2O
The decahydrates form of borax can also be used as a standard solution for titrimetric analysis as it is highly stable and pure.
Natural Sources of Borax
Natural sources of borax include evaporite deposits formed by the frequent evaporation of seasonal lakes. Turkey, Boron, California, and Searles Lake, California, have the most commercially significant deposits. Furthermore, borax has been discovered in many other locations throughout the Southwest United States, the Atacama desert in Chile, and newly discovered deposits in Bolivia and Tibet, and Romania. Borax can also be synthesized from other boron compounds.
Other Uses of Borax
- As a pH buffering agent in swimming pools to control the pH of the water
- As a co-complexing agent
- As a water-softening agent
- For gold extraction in small-scale gold mining
- As a food additive
- As an ingredient in enamel glazes
- As a component of glass and ceramics
- As a fire-retardant
- As a flux in metal and alloys melting removes impurities and inhibits oxidation
- As a neutron absorber, which is used in nuclear reactors to regulate reactivity and stop nuclear chain reactions.
| Properties | Borax | Baking Soda |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | Na2B4O7·10H2O | NaHCO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 381.37g/mol | 84g/mol |
| Appearance | White, crystalline solid | White crystals |
| pH Value | 9.5 | 8 |
| Melting Point | 743°C (anhydrous) 75°C (decahydrate, decomposes) | Decomposes to sodium carbonate starting at 50 °C |
| Boiling Point | 1,575°C (anhydrous) | 851 °C |
| Density | 1.73 g/cm3 | 2.20 g/cm3 |
| Solubility In Water | 31.7 g/L | 69 g/L (0°C), 96 g/L (20°C),165 g/L (60°C) |
| Safety Hazards | It should not be consumed, inhaled or exposed to the skin. | It is safe to consume. |
Can Borax And Baking Soda Be Mixed?
To remove tough, set-in stains, a borax, and baking soda mixture can be a helpful cleaning solution. This method combines one teaspoon of borax and one teaspoon of baking soda in a bowl. Pour half a glass of hot water and stir until the ingredients dissolve. Then, use a sponge or cloth to scrub the paste onto the stain.
Together, they are the best way to clean laundry. To use this method, fill the bathtub with warm water and add a mixture of baking soda, borax, and laundry detergent. Allow 30 minutes for your laundry to soak before washing it as usual. This method is ideal for towels, bedsheets, and other linens, but it can also be used cautiously on clothes.
What Can Borax Be Combined With?
A mixture of vinegar and borax is an excellent option for a safe and effective cleaning solution. They help clean surfaces and remove mildew. When mixing the two ingredients, use warm water to help the borax dissolve more easily.
Which One is Better?
Since both the compounds are alkaline and abrasive, they’re quite effective as cleaning agents. However, borax has a relatively high pH; thus, it is a slightly tougher but potentially more effective cleaning agent. It is antifungal, antimicrobial, and antibacterial.