Nuclear Power Safety: Boron and Neutron Capture
Nuclear power is a controversial topic. Many want to abolish it entirely. And just as many believe that the benefits of nuclear power outweigh its risks. But in any case, there can be no denying that the safety of nuclear reactors is paramount for both sides of the argument. That is why we’re going to take a closer look at boron today. It is one of the most important materials in neutron capture for nuclear power safety.

Nuclear Power
Boron: Neutron Capture for Nuclear Power Safety
Boron has no electrons and, therefore, offers immense potential to contribute towards nuclear safety. Its ability as a neutron capture agent helps prevent the release of neutrons from the reactor core in an uncontrolled manner.
In addition, neutron capture agents help to control the rate at which neutrons are emitted by slowing them down to thermal energies. Here, they are absorbed by moderating materials like water or graphite. Its high chemical activity also helps with this process as it promotes fission reactions in uranium fuel pellets. Therefore, it reduces heat generation within the fuel rods while still producing energy through fission.
Boron is a powerful neutron capture agent due to its high reactivity with hydrogen. When neutrally charged boron atoms interact with molecules containing H2, their electric charge rises. They form strong bonds that give off heat- key to preventing the dangerous magnetic fields that lead to potentially lead shutdowns in nuclear reactors.
Additionally, Boron not only helps nuclear power safety. There is research on this element in different applications. It includes:
- Agriculture: pesticides, fertilizers, insecticides;
- Petrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, synthetic fibers, and textile dyes.
- Semiconductors/electronics industry components like transistors and semiconducting devices.
- Production of high-strength structural composites.
- Coal power industry.
Why is Boron Important to Nuclear Power Safety?
Boron is important to nuclear power safety for several reasons. It is useful in the production and refining process of uranium hexafluoride. Research shows that it can increase neutron capture cross sections by more than two orders of magnitude. This means its ability to slow down neutrons makes it ideal for studying how to manage radioactive waste.
In addition to this function, it prevents recombination reactions that lead to magnetic fields which can potentially cause reactor shutdowns.
How Does Boron Work in a Nuclear Reactor?
The role of Boron in a nuclear reactor is to control the activity and function of fuel rods. It can slow down neutrons, preventing them from passing through the reactor core without using up their energy. Some reactors also use boron as a neutron absorber to act as an emergency shutdown mechanism.
The Benefits of Including Boron in Nuclear Power Plants
Boron is an essential element that can reduce safety hazards. It reduces radioactive emissions and prevents reactions that lead to dangerous magnetic fields. Thus, it helps with the long-term storage of radioactive waste. In addition, it helps make sure there are no leaks or ruptures within containment structures.
The boron properties help to prevent radioactive emissions, which are harmful. This benefits the people living near a nuclear power plant.
Borax, or sodium tetraborate (NaB), is a useful tool in ensuring safety at nuclear power plants. Because it absorbs neutrons more easily than any other substance on Earth, even uranium.
The Future of Boron as a Neutron Absorber in Reactors
Boron as a neutron absorber is a promising solution to the safety concerns around nuclear power.
The future of using boron as a neutron absorber in reactors is promising for nuclear power’s safety. You can resolve measurement issues with more research into understanding neutrons. It is important to understand how they are absorbed. Hence, the reactor operators have better control over this process when it comes time to use borates on-site at their plant.
Possible future uses of boron in nuclear power may include:
- A type of emergency shutdown system. Here, if operators have trouble with their controls they can add more absorbers and try again.
- Borates as part of an emergency cooling system. It is activated during a meltdown scenario because it’s important to cool down the fuel rods quickly before too many fission products are released into the atmosphere.
How to Ensure that the Reactor is Safe from Meltdown?
The quantity of Boron is a key issue. A second independent coolant system using borates and a third passive cooling system (freeze plugs) provides the necessary emergency cooling loops for a longer duration.
But it is unclear how much Boron is enough to keep the reactor safe from a meltdown.
What other Benefits does it have?
Boron is useful in different things, including satellites, aircraft, and emergency medical equipment. Because it absorbs neutrons more easily than uranium too. This makes it an essential ingredient in certain medicines like low-dose radiation treatment for cancer patients and chemotherapy. In chemotherapy, boron kills cancer cells. It also helps to prevent the formation of new blood vessels that are necessary for tumors.
Boron is an effective cancer treatment agent. Studies show that it helps cancer patients live longer than they would without receiving the therapy.
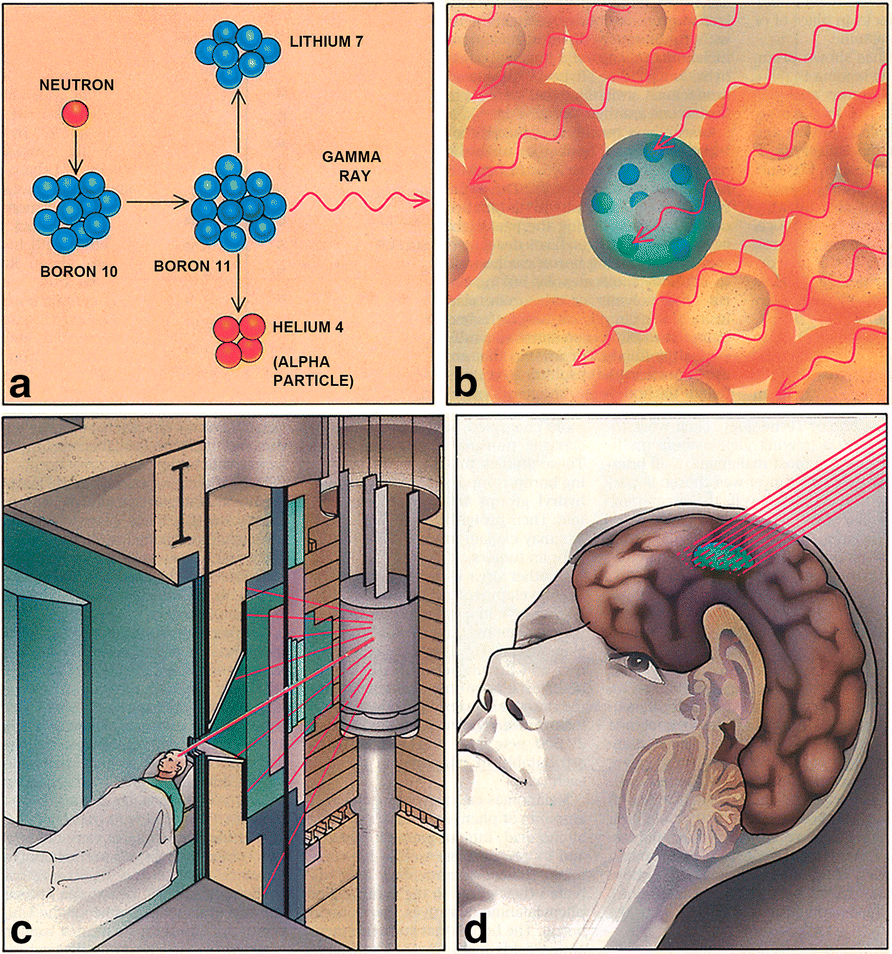
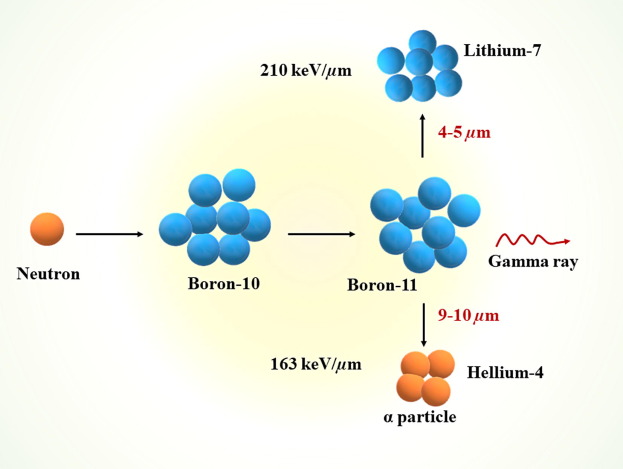
Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT)
Doctors bombard a patient’s tumor with neutrons to produce high-energy gamma rays that kill cancer cells. These treatments are usually given one or more times per week and can last for months. It depends on the severity of the disease. Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT) has cleared many types of cancers in clinical studies, including brain tumors, lung cancer, prostate cancer, and breast cancer, among others.
Takeaways
The use of borons in neutron capture helps make nuclear power much safer than before. It has fewer risks and less accumulation of radioactive substances within reactors compared to other types of reactor technologies. Uranium fuel rods or open pools of water contain unshielded high-level radioactive waste materials.
The safety of nuclear power plants is essential in our modern world. We can continue to explore the possibilities of discovery and use of this resource. But we need to know how any discoveries might affect current practices. This article has shown you some ways that boron could help make a safer plant environment with less risk of release into the atmosphere or groundwater.