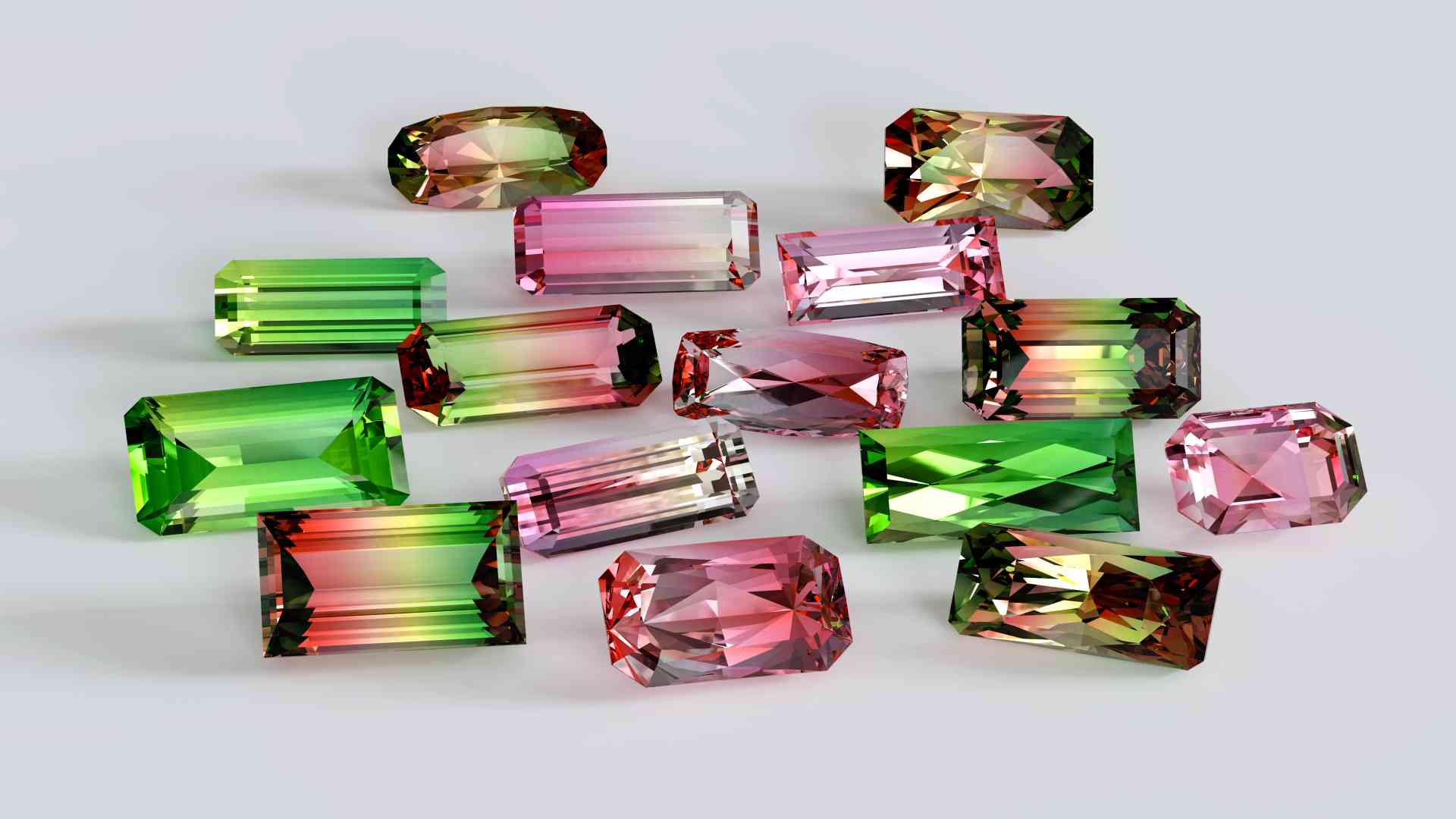
Tourmaline A Mineral Worth Knowing
Tourmaline is a group of boron silicate minerals with similar physical properties and a standard crystal structure, but the minerals vary widely in chemical composition. A wide variety of compositions, trace elements, and shade facilities causes these minerals to occur in more colors and color combinations than any other mineral group.

Tourmaline
Tourmaline Properties
1. Chemical Characteristics
Tourmaline is a complex group of silicate minerals with varied compositions due to the isomorphous replacement. The general chemical formula is presented as XY3Z6(T6O18)(BO3)3V3W, where
X = Ca, Na, K
Y = Li, Mg, Fe2+, Mn2+, Zn, Al, Cr3+, V3+, Fe3+, and Ti4+
Z = Mg, Al, Fe3+, Cr3+, V3
W = OH, F, O, and
V = OH, O
T = Si, Al, B
Role of Boron in Silicate Minerals
- Metal borides and boron hydrides from deep-seated mantle levels formed tourmaline-quartz-type gold deposits distributed in the earth’s crust.
- These minerals inside the Qiman Tagh belt wall rocks have δ11B values that vary from -11.1% to -7.1%, suggesting a source of metasediments devoid of marine evaporates.
- Minerals hosted in monzogranite have 11B values ranging from -10.7% to -9.2%. These values correspond to those found in continental crust sediments, suggesting a possible connection between the two as the wall rocks and the monzogranite are formed under similar conditions.
- Together with the elemental diagrams and geological features, minerals of quartz veins have 11B values between 11.0 and 9.6, confirming a similar granite-derived origin for the quartz veins and negligible B isotopic fractionation.
2. Physical Characteristics
| Properties Name | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Chemical Classification | Boron Silicate |
| Category | Cyclosilicate |
| Crystal System | Trigonal |
| Color | The most frequent color is black. Furthermore, it can be found in blue, green, red, pink, orange, yellow, purple, crimson, and even colorless. Single crystals frequently have zones. |
| Mohs Hardness | 7 to 7.5 |
| Density | 2.8 to 3.3 |
| Luster | Vitreous |
| Diaphaneity | Translucent to nearly opaque |
| Streak | White |
| Tenacity | Brittle |
3. Optical Characteristics
| Properties Name | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Refractive Index | nω = 1.635–1.675 nε = 1.610–1.650 |
| Birefringence | 0.018 to −0.040; typically about −0.020 but in dark stones it may reach −0.040 |
| Pleochroism | Typically moderate to strong Red: definite; dark red, light red Green: strong; dark green, yellow-green Brown: definite; dark brown, light brown Blue: strong; dark blue, light blue |
| Dispersion | 0.017 |
| Ultraviolet fluorescence | Pink stones; inert to very weak red to violet in long and short wave |
| Absorption spectra | Blue and green stones exhibit a strong narrow band at 498 nm and practically perfect red absorption down to 640 nm; red and pink stones exhibit lines at 458 and 451 nm and a broad band in the green spectrum. |
4. Metaphysical Characteristics
These gemstones stone have long been associated with love and emotional healing. Its unique metaphysical properties make it a powerful tool for helping to dissolve negative emotions and restoring balance to relationships. Additionally, it is regarded as an aphrodisiac and encourages mental flexibility and openness.
These gemstones are believed to be powerful in all colors and affect each person differently.
Pink Tourmaline
The pink version is considered to encourage improved listening and understanding, making it the perfect stone for healers and counselors. It embodies the virtues of friendship and everlasting love. For others, the pink-colored gemstone symbolizes compassion and humanitarianism. It is also a powerful ally for those who experience panic attacks and have difficulty with anxiety. The soothing vibration of the stone helps alleviate inner conflict and fear while developing sympathy for others.
Black Tourmaline
It is a powerful stone that can help to repel negative energy and promote positive change. This stone can also be helpful in times of crisis or extreme stress, as it can enhance inner wisdom, stability, courage, and patience.
Blue Tourmaline
It builds a dedication to accomplishing one’s goals and safeguarding the wearer from dangers.
Red Tourmaline
It promotes inner strength and wisdom by uniting the heart and body through love and passion. It also helps with open-mindedness, emotional stability, compassion, and devotion.
Watermelon Tourmaline
It is a stone of reconciliation, i.e., a stone that encourages compassion and cool-headedness, radiates the energy that fascinates money, healing, and friendship, stabilizes grounds, and reaffirms our Earth roots.
Different Types of Tourmaline Crystal
1. Schorl
Schorl is the most prevalent species, accounting for 95% or above of all minerals found naturally. The early history of the mineral schorl reveals that the word “schorl” was first used in 1400 when a village now known as Zschorlau was named “schorl” after the black tourmaline was discovered in nearby tin mines.
2. Elbaite
Lithium-tourmaline elbaite was discovered in Utö, Sweden. This is unique because it contains lithium, which Johan August Arfwedson found in 1818. Elba Island in Italy was one of the first places where colorful and colorless Li-tourmaline was chemically studied. In 1972, Donnay and Barton published the first crystal identification of these minerals conducted on a pink elbaite from California.
3. Dravite
Gustav Tschermak coined the term dravite for the first time. It is the sodium and magnesium-rich tourmaline endmember, also known as brown tourmaline. In contrast, uvite is a calcium-magnesium tourmaline. Dravite forms several series with other minerals like schorl and elbaite. Discovered in 1884 by Austrian mineralogist Gustav Tschermak, dravite is a variety of tourmalines that gets its name from the Drava River area in Austria and Slovenia. Deep green chromium dravite and vanadium dravite are the two main dravite varieties.
Benefits of Wearing a Tourmaline Stone
This beautiful and popular gemstone is well-known for its healing properties.
- It prevents electromagnetic pollution,
- Avoids negative energy,
- Improves grounding,
- Boosts physical energy,
- Improves immune system, and
- Provides relief in arthritis pain.
How did this Gemstone Evolve?
Tourmaline mineral came from the Sinhalese term “turmali,” which was used to describe all colored crystals on the island of Sri Lanka. Dutch traders discovered this stone off the West Coast of Italy in the late 1600s or early 1700s. This all-encompassing name reflects the inability of ancient gem dealers to distinguish tourmalines from other stones. Red and pink tourmalines, for example, were once thought to be rubies. Pink gemstone is known as the birthstone for October.