Optibor Boric Acids
Optibor boric acids (H3BO3) are pure, multi-functional boric oxide sources (B2O3). They are the most common industrial borate and are available in granular or powder form. Under normal conditions, these are stable, free-flowing, and easy to handle. They are mildly acidic in solution.
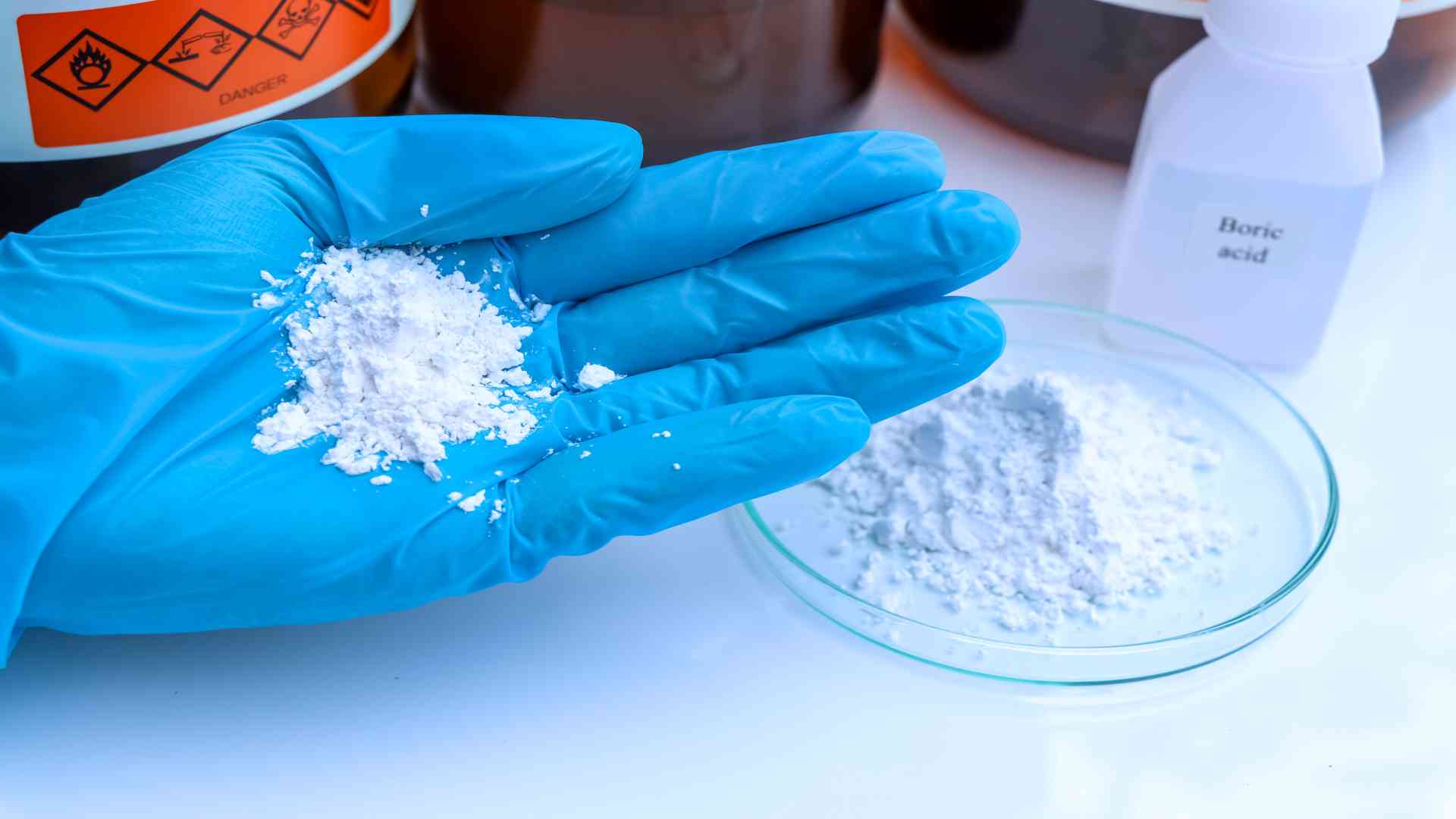

Optibor
Physical and Chemical Properties
Optibor Specifications
Chemical formula H3BO3
Chemical Name Boric acid, Orthoboric acid, Boracic acid
Molecular Weight 61.84 g/mol
Specific Gravity 1.51
Melting Point 170.9°C
Appearance White, Odorless, Crystalline solid
Vapour Pressure Negligible at 20°C
Solubility 4.7% at 20°C; 27.5% at 100°C
pH at 20°C 6.1 (0.1% solution); 5.1 (1.0% solution); 3.7 (4.7% solution)
Source: Wikipedia
Optibor boric acids gradually lose water when heated above 100°C (212°F), changing to metaboric acid, HBO2.
Unless the heating time is extended or the temperature is raised above 150°C (302°F), dehydration stops at the composition HBO2.
All water is removed as the temperature rises, leaving only the anhydrous oxide, B2O3, whose crystalline form melts at 450°C (842°F).
The amorphous form has no fixed melting point, softening at approximately 325°C (617°F) and becoming fully fluid at about 500°C (932°F).
Stability
Optibor is a chemically stable crystalline product that does not change under normal storage conditions. Temperature and humidity fluctuations cause recrystallization at particle contact points, resulting in caking. As a result, caution should be exercised to avoid such fluctuations during product storage. It is also necessary, of course, to maintain the packaging’s integrity.
Reactivity
It is a weak acid, which can cause base metal corrosion. It reacts with strong reducing agents, such as metal hydrides or alkali metals, to produce hydrogen gas, which can be explosive.
Many Advantages
1. Glasses And Fiberglass
Boron oxide (B2O3) is used as a flux and network former in the optibor process. This helps lower the glass’s melting temperature and improve its fiberization properties. Furthermore, it improves the glass’s durability and chemical resistance. It is often combined with sodium borate (borax pentahydrate or anhydrous borax) to adjust the sodium to boron ratio in glasses that need low sodium levels. This is essential in borosilicate glass, where B2O3 offers excellent fluxing properties at low sodium and high alumina levels.
2. Metallurgy
Optibor inhibits metal surfaces from oxidizing during welding, brazing, or soldering. It is also used as a boron source for metal alloys and steel strengthening.
3. Adhesives and Sealants
Optibor is a crosslinking agent that significantly improves starch-based adhesives’ tack and green strength. It is also used as a peptizing agent for manufacturing casein-based and dextrin-based adhesives. Its unique ability to crosslink the hydroxyl group is an essential ingredient in many adhesive formulations.
4. Corrosion Protection
Optibor is used in various aqueous and non-aqueous systems that require corrosion protection, lubrication, or oxidative thermal stabilization. It is also used for manufacturing lubricants, metalworking fluids, brake fluids, water treatment chemicals, and fuel additives.
5. Flame Retardancy
Borates help minimize the flammability of cellulose insulation, wood composites, and mattress cotton batting. When introduced into cellulose materials, borates alter the oxidation reactions and lead to char formation, which inhibits combustion. Optibor is particularly effective in this regard, either alone or combined with borax.
6. Pharmaceutical Uses
The pharmaceutical industry is a vital sector of the economy, and producers rely on high-quality borax products to manufacture their drugs and medicines.
7. Frits, Glazes, and Enamels
Boric oxide is a critical component in the production of ceramics and enamels. It functions as a network of former and flux, initiating glass formation and ensuring a thermal fit between the glaze and the body. Boric oxide also improves refractive index, strength, durability, and scratch resistance while decreasing viscosity and surface tension. High boron frits develop quickly and make suitable bases for coloring oxides. In the formulation of fast fire frits for tiles, optibor boric acids are used as a B2O3 source. These boric acids speed us the development of smooth and even gaze surfaces.
8. Personal Care Products
Optibor is used in personal care products such as cosmetics, toiletries, and pharmaceuticals. It is used to buffer pH with sodium borates and as a crosslinking agent to emulsify waxes and other paraffin.
9. Metals and Gold
Borates aid in the protection of ferrous metals from oxidation and the hardening of steel.
10. Wood Protection And Fungi
Borates and boron compounds provide fire, fungi, and pest resistance to wood products.
11. Nuclear Energy
The boron-10 isotope, as a highly effective high neutron absorber, is critical to nuclear power plant safety and control systems. The nuclear industry uses its SQ and HP grades, which can be isotopically nourished to enhance the available proportion of boron-10.
12. Chemical Reactions
Optibor catalyzes hydrocarbons oxidation and enhances alcohols yields in the manufacture of nylon intermediates by forming esters that further inhibit hydroxyl groups oxidation to ketones and carboxylic acids.
It is also used for producing essential industrial products, including boron halides, borohydride, metallic borates, borate esters, and boron-containing ceramics.
13. Other Applications
- Dye stabilization
- Sand-casting (magnesium)
- Electrolytic capacitors
- Textile finishing
- Leather processing and finishing
- Electroplating
- Paints
Potential Health Effects With Optibor
Exposure Routes: Inhalation is the most common route of exposure in occupational and other environments. Because optibor is poorly absorbed through skin contact, dermal exposure is generally not a concern.
Inhalation: Its dust inhalation at levels greater than 10 mg/m3 may cause mild irritation to the nose and throat.
Eye Contact: It is non-irritating to the eyes in regular industrial use.
Skin Contact: It does not irritate healthy skin.
Consumption: Its products are not intended for consumption. It has low acute toxicity. Small amounts accidentally ingested are unlikely to cause effects; larger quantities may cause gastrointestinal symptoms.
Cancer: It is not known to cause cancer.
Reproductive/Developmental Effects: Several species’ animal ingestion studies show that borates have reproductive and developmental effects. A human study of occupational exposure to borate dust revealed no adverse effects on reproduction.
Target organs: In humans, no target organ has been identified. According to high-dose animal ingestion studies, the testes are the target organs in male animals.
Signs and Symptoms of Exposure
Symptoms of accidental overexposure occur due to consumption or absorption through many areas of damaged skin. These can include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and skin redness and peeling.
Reference article – Optibor Boric Acid